Fibromas
Fibromas
Why do fibroids develop?
Fibromas are benign nodules (“neoplasms”) composed of connective or other supporting tissue. A fibroma is an expression of excessive activity of cells that form connective tissue, called fibroblasts. These cells are found in all connective tissues of the human body. A fibroma is benign, so it is not cancer.
Where do fibromas occur?
Fibromas usually occur sporadically and only in certain areas of the body; however, when they extend over the entire body, physicians refer to them as fibromatosis.
Most often, a fibroma develops on the surface of the skin without any apparent cause. Treatment is often not necessary because fibromas usually do not cause any symptoms. Nevertheless, it is advisable to consult a doctor, especially in the case of newly appeared lumps – he can often recognize harmless fibromas at a glance.
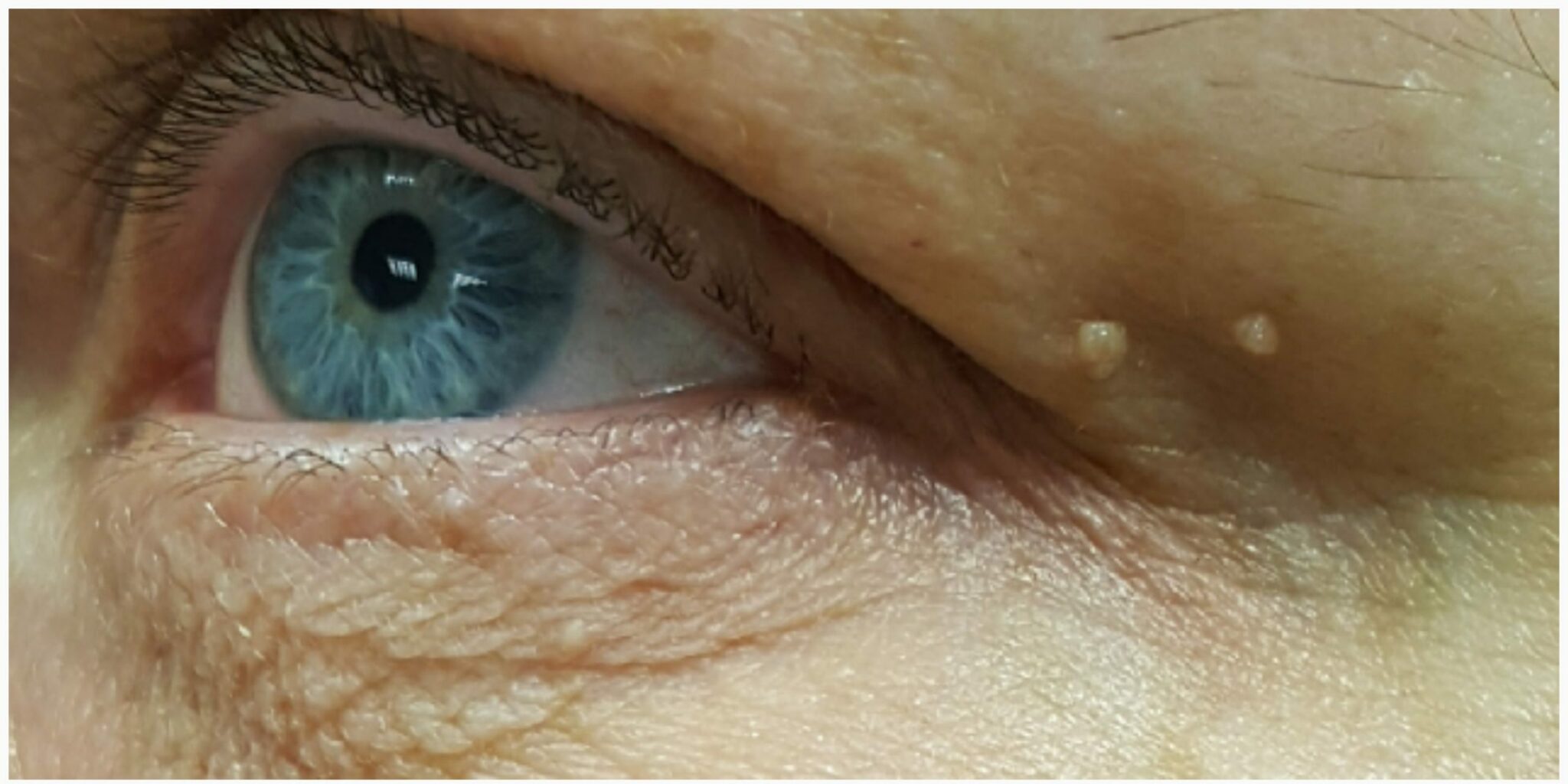
Forms and types
Fibroma: pedunculated nipple
Soft fibromas (fibroma molle) are usually stalked protrusions (fibroma pendulum) of the skin that are otherwise little to no different in appearance from the surrounding tissue. These appendages are located preferentially on the eyelids, neck or armpits of almost every middle-aged person. They can be a few millimeters to several centimeters in size and sometimes brownish in color. Soft fibromas are also colloquially referred to as pedunculated warts, as they often protrude from the skin like a stalk.
Hard fibroma
Hard fibromas (fibroma durum), on the other hand, protrude only slightly above the skin level (papule), since the connective tissue here proliferates in a deeper skin layer. They can be skin-colored, pink or brown in color and appear primarily on the legs.
Symptoms
A fibroma usually protrudes from the skin, which is why it is also called a pedunculated wart. Usually the skin growths are skin colored or darker. However, if they are rotated, blood vessels may be injured, causing them to turn blue-red or even black. Especially very large or particularly many fibromas can significantly affect the appearance. Some fibromas are accompanied by symptoms such as sensitivity to pain and pressure when touched.
Treatment
In order to make an exact diagnosis, the doctor can examine the tumor more closely with a special magnifying instrument (dermatoscope). If it is still not clear whether it is a fibroma or not, a dermatologist may be able to take a tissue sample (biopsy). This usually involves complete removal of the tumor under local anesthesia and subsequent examination of the tissue under a microscope.
Because fibroids are often located in visible areas of the body, they can be an aesthetic problem. If necessary, a pedunculated nipple can be surgically removed for treatment. The removal of a fibroid is not very complex and has few complications. Nevertheless, you should avoid removing pedunculated nipples yourself at all costs, as there is a higher risk of infection.
In addition, there is a non-inversion procedure of the skin to remove warts.
Papilloma
Papilloma is a benign tumor that originates from the uppermost layers of skin or mucous membrane of an organism. Papillomas are found, for example, on the skin of the body surface, in the urinary tract, in the excretory ducts of the female breast and other glands, or on the mucous membranes of the mouth, nose, sinuses, or gastrointestinal tract (villous adenoma). Papillomas have a cauliflower-like appearance and can grow up to one centimeter in size. Histologic examination reveals a vascular, finger-shaped branching stroma with regular superficial squamous epithelium. The cause is thought to be viral infections or mechanical irritation.
